Overview
Medial Patellofemoral Ligament (MPFL) Reconstruction Surgery
Reconstruction of the medial patellofemoral ligament (MPFL) is for patients who may have experienced a tendon tear that is causing recurring knee patellar instability. MPFL injury is commonly attributed to acute traumatic patellar dislocation—when the knee cap suddenly moves out of place.
A common sign that surgery may be necessary, is continued knee instability despite attempts at non-operative treatment. Nonsurgical treatment usually includes wearing a brace in conjunction with targeted physical therapy. Reconstructive surgery is also considered as a solution if you are suffering from a mild bone malalignment.
Your MPFL is: A tendon on the inside of your knee’s medial side that connects your kneecap (patella) to your thigh bone (femur), and stabilizes your knee by preventing lateral displacement of your kneecap.
Bone malalignment: The displacement of bones out of line in relation to joints.
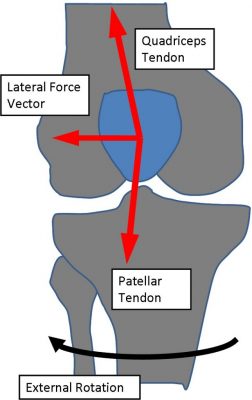
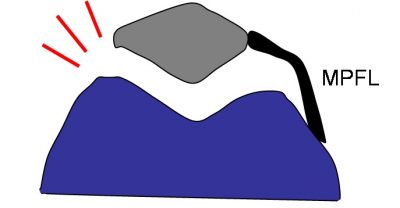
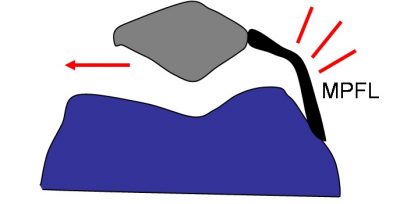
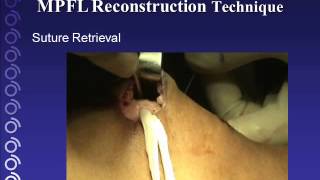
The Facts on MPFL Reconstructive surgery:
- Lateral patella dislocations are common injuries seen in active young patients.
- It is necessary to treat associated cartilage injury in conjunction with the MPFL reconstruction surgery
- Patients who may not respond well to MPFL reconstruction are those with extreme malalignment and patellofemoral arthritis. Dr. Ahmad offers other procedures in these situations
- An MRI is the most common means to assess MPFL damage
Symptoms:
The following symptoms are commonly reported from patient with an MPFL injury:
- Feeling unstable, or shaky when using the affected knee
- A sensation that the kneecap is moving to the side during movement
- Swelling of the knee
- Restricted range of motion
- Pain when moving the joint
- Pain, stiffness, or “locking,” after sitting for a prolonged period of time.
Evaluation by Team Ahmad
Dr. Ahmad and his team of health professionals will greet you and start your visit with a discussion of your symptoms, sport, level of competition, desired activity level, and mechanism of injury. Next, the doctor will exam your knee, focusing on:
- The severity of swelling
- Range of motion
- MPFL tenderness
- Muscle strength
- General knee alignment
- Degree of looseness of the patella
In some situations, Dr. Ahmad may order an MRI scan to determine the severity of the MPFL tear.
Treatment Options
When you elect to have reconstructive surgery to repair your damaged MPFL, your procedure will typically include two phases, the first being the actual surgery, and the second being the process of recovering properly form the surgery. This second phase is known as the rehabilitation phase.
Surgical
Reconstructive surgery of an MPFL tear generally includes:
- Diagnostic Arthroscopy: A procedure used to assess the damage to your knee and its tendons, specifically it looks for any intra-articular abnormalities, including cartilage damage around the kneecap joint.
- Chondroplasty: If cartilage damage is found, this procedure uses a small instrument to shave off cartilage flaps. Some situations require cartilage restoration. Please visit {Insert Link} for more information.
- Reconstruction: This entails making incisions to expose the MPFL, and using screws and pins to realign and reattach the kneecap and the torn tendon.



Rehabilitation and Recovery
One of the most important parts of surgery is the post-operation recovery process, known as rehabilitation or rehab. For MPFL reconstructive surgery rehab is focused on achieving the following 12-week initial rehab goals:
Weeks 1 through 6:
- Weight bearing in extension.
- A home program for quadriceps strengthening is started
Week 2 through 6
- Formal physical therapy begins, including passive and active-assist range of motion.
Week 6
- Physical therapist begins more aggressive strengthening of the quadriceps and hamstrings, as well as hip and core muscles.
Week 12
- Running and agility training is permitted, and a return to full athletics may be anticipated starting at 4 months.
Dr. Ahmad’s Experience
Dr. Ahmad is nationally recognized expert in patella instability surgery and has designed and studied the optimal methods to surgically correct patella instability. His undergraduate training in mechanical engineering has allowed him to research the optimal methods of treatment. Dr. Ahmad has performed several hundred patella instability surgeries and has treated all types of patients from elite professional athletes to recreational athletes who sustained patella dislocations.
Listed below is Dr. Ahmad’s scholarly articles and research published to help patellar instability treatment.
Dr. Ahmad’s Scholarly Publications Related to Patella Dislocations
Peer Reviewed Scientific Journal Articles
- Franzone J, Vitale M, Shubin Stein BE, Ahmad CS: Is there an Association between Chronicity of Patellar Instability and Patellofemoral Cartilage Lesions: An Arthroscopic Assessment of Chondral Injury, Journal of Knee Surgery, 25:411-416, 2012
- Ahmad CS, Brown GD, Stein BS: The Docking Technique for Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction: Surgical Technique and Clinical Outcome. American Journal of Sports Medicine, 37:2021-2027, 2009
- Trentacosta NE, Vitale MC, Ahmad CS: The Effects of Timing of Pediatric Knee Ligament Surgery on Short-Term Academic Performance in School-Aged Athletes. American Journal of Sports Medicine, 37:1684-1691, 2009
- Ahmad CS, McArthy M, Gomez J, Shubin Stein BS: The Moving Patella Apprehension Test for Lateral Patellar Instability. American Journal of Sports Medicine, 37:791-796, 2009
- Brown GD, Ahmad, CS: Combined Medial Patellofemoral Ligament and Medial Patellotibial Ligament Reconstruction in Skeletally Immature Patients. Journal of Knee Surgery, 21:328-32, 2008
- Ahmad CS, Sincropi SM, Su B, Puffinbarger W: Congenital Medial Dislocation of the Patella: A Case Report. Orthopedics, 26:189-190, 2003
- Ahmad CS and Lee FY: An All-Arthroscopic Soft Tissue Balancing Technique for Lateral Patellar Instability. Arthroscopy, 17:555-557, 2001
- Ahmad CS, Cohen ZA, Levin e WN, Ateshian GA, Mow VC: Biomechanical and Topographic Considerations in Autologous Osteochondral Grafting in the Knee. American Journal of Sports Medicine, 29:201-206, 2001
- Ahmad CS, Shubin Stein BE, Matuz D, Henry J: Immediate Surgical Repair of the Medial Patellar Stabilizers for Acute Patellar Dislocation: A Review of Eight Cases. American Journal of Sports Medicine, 28:804-810, 2000.
- Kwak SD, Ahmad CS, Gardner TR, Grelsamer RP, Henry JH, Blankevoort L, Ateshian GA, Mow VC: Effects of Hamstring and Iliotibial Band Forces on Tibial and Patellar Kinematics and Contact. Journal of Orthopedic Research, 18:101-108, 2000
- Ahmad CS, Kwak SD, Ateshian GA, Warden WH, Steadman JR, Mow VC: Effects of Patellar Tendon Adhesion to the Anterior Tibia on Knee Mechanics. American Journal of Sports Medicine, 26:715-724, 1998
- Raimondo RA, Ahmad CS, Blankevoort L, April EW, Grelsamer RP, Henry JH: Patellar Stabilization: Quantitative Evaluation of the Vastus Medialis Obliquus Muscle. Orthopedics, 21:791-795, 1998
Published Extended Abstracts
- Cohen ZA, Ahmad CS, Roglic H, Levine WN, Henry JH, Ateshian GA, Mow VC: Biomechanical Considerations for Autologous Osteochondrol Grafting of the Femoral Articular Surface. American Society of Mechanical Engineers BED, 42: 129-130, 1999
- Kwak SD, Ahmad CS, Gardner TR, Wu H, Grelsamer RP, Henry JH, Blakevoort L, Mow VC: Tibiofemoral and Patellofemoral Kinetics and Contact: Effects of Hamstrings and Iliotibial Band Force. American Society of Mechanical Engineers BED, 31: 41-42, 1997
- Kwak SD, Ateshian GA, Blankevoort L, Ahmad, CS, Gardner TR, Grelsamer RP, Henry JH, Mow VC: A General Mathematical Multibody Model for Diarthrodial Joints: Application and Validation Using the Patellofemoral Joint. American Society of Mechanical Engineers BED, 31: 239-240, 1996
- Kwak SD, Blankevoort L, Ahmad CS, Gardner TR, Grelsamer RP, Henry JH, Ateshian GA, Mow VC: Anatomically Based 3-D Coordinate System for the Knee Joint. American Society of Mechanical Engineers BED, 31: 309-310, 1995
- Ateshian GA, Cohen ZA, Kwak SD, Wang VM, Ahmad CS, Kelkar R: Determination of In-Situ Contact Areas in Diarthrodial Joints by MRI. American Society of Mechanical Engineers BED, 31: 225-226, 1995
- Ahmad CS, Frenkel, Sally R, Casar RS, Alexander H: Mechanical Testing Technique for Articular Cartilage: A Study of Intrinsic Repair. American Society of Mechanical Engineers BED, 22: 379-382, 1992
Editorials and Letters to the Editor
- Ahmad CS: Regarding the Etiology Patellofemoral Dysfunction Following ACL Reconstruction. American Journal of Sports Medicine, 29:789-790, 2001
- Ahmad CS: Regarding Patellar Dislocations. American Journal of Sports Medicine 29:389-391, 2001
Review Articles, Current Concept Articles and Surgical Techniques
- Boselli K, Shubin Stein B, Ahmad CS: Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction: Docking Technique, Operative Techniques in Sports Medicine: Ahmad, Guest Editor: Elsevier, Illinois, 18: 98-106, 2010
- Gardner TR, Comron, Ahmad CS: Anatomy and Biomechanics of Patellar Instability, Operative Techniques in Sports Medicine: Ahmad, Guest Editor: Elsevier, Illinois, 18: 62-67, 2010
- Brown M, Schulz B, Ahmad CS: Evaluation and Imaging of the Patellofemoral Joint, Operative Techniques in Sports Medicine: Ahmad, Guest Editor: Elsevier, Illinois, 18: 68-78, 2010
- Brown GD, Ahmad CS: The Docking Technique for Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction. Operative Techniques in Orthopaedics, 17:216-222, 2007
Textbooks/Guest Editorship
- Ahmad CS, Editor: Sports Medicine 2. Instructional Course Lectures Sports Medicine Specialty Volume 2: American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, Illinois, 2011
- Ahmad CS, Shubin Stein BE Guest Editor: Patellar Instability. Operative Techniques in Sports Medicine. Elsevier, Illinois. Vol 18, pp 61-128, 2010
- Ahmad CS, Editor: American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Monograph Series. Pediatric and Adolescent Sports Injuries. American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, Rosemont. Series 43, pp 1-199, 2010
- Levine WN, Ahmad CS, Editors: Management of the Patellofemoral Joint. Operative Techniques in Orthopedic Surgery. Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia. Vol 17, pp 203-264, 2007
Book Chapters
- Brafman RT, Fabian L, Ahmad CS: Knee Ligament Injuries in Young Athletes, American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Monograph Series. Management of Common Sports Injuries in Pediatric and Adolescent Patients: Ahmad CS, Editor: American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, Illinois, 2010
- Shubin-Stein BE, Ahmad CS: Patellofemoral Disorders, Sports Medicine: Schepsis A, Editor: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Maryland, 2006
- Ahmad CS, Yamaguchi K, Wolf I, Bigliani LU: The Shoulder, Sports Medicine: A Comprehensive Approach 2nd edition: Scuderi and McCann, Editor: Mosby, Inc., Philadelphia, 2005
- Ahmad CS, Levine WN, Blaine TA: Essentials of Musculoskeletal Imaging: Johnson TR and Lynne S. Steinbach, Editors: American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons , Rosemont, 2004
- Ahmad CS, ElAttrache NS: Acute Elbow Injuries, Orthopaedic Knowledge Update: Sports Medicine 3:Garret W, Editor: American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, Chicago, 2004